Residential Flat Roof Repair A Practical Guide
Residential flat roof repair can seem daunting, but understanding the common issues and repair methods empowers homeowners to tackle problems effectively. This guide walks you through identifying problems, choosing the right materials, and performing repairs, ultimately extending the life of your roof and saving you money. We’ll cover everything from identifying leaks to choosing the best repair materials for your budget and climate.
From recognizing the telltale signs of damage like sagging, blistering, or ponding water, to understanding the lifespan differences between EPDM, TPO, and modified bitumen roofing, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. We’ll also explore preventative maintenance strategies to keep your roof in top condition for years to come.
Common Residential Flat Roof Problems

Source: threebrothersroofingrepairs.com
Flat roofs, while offering design advantages, require regular maintenance and attention to prevent costly repairs. Understanding common issues and their causes is crucial for homeowners to proactively address potential problems and extend the lifespan of their roof. Ignoring problems can lead to significant water damage and structural issues.
Frequent Causes of Flat Roof Leaks
Several factors contribute to leaks in residential flat roofs. Understanding these common causes allows for targeted preventative measures and quicker identification of problems.
- Poor Installation: Improper installation is a leading cause of leaks. This includes inadequate flashing around penetrations (chimneys, vents, pipes), insufficient sealing of seams, and incorrect slope for proper drainage.
- Aging and Deterioration of Roofing Materials: Over time, all roofing materials degrade. Exposure to UV rays, temperature fluctuations, and moisture weakens the membrane, leading to cracking, blistering, and ultimately, leaks.
- Ponding Water: Poor drainage can cause water to accumulate on the roof surface, putting excessive stress on the membrane and increasing the risk of leaks. This is exacerbated by debris blocking drains.
- Damage from Debris and Impact: Falling branches, hail, or other debris can puncture or damage the roofing membrane, creating entry points for water.
- Improper Maintenance: Neglecting regular inspections and maintenance, such as cleaning debris and addressing minor repairs promptly, can allow small problems to escalate into major leaks.
Signs of Flat Roof Damage
Recognizing the signs of damage is essential for timely repairs. Early detection can prevent extensive and costly repairs later on.
- Visible Cracks or Tears: These are clear indicators of membrane damage and potential leaks. Cracks can be small and hairline, or large and gaping.
- Blisters or Bubbles: These often indicate moisture trapped beneath the roofing membrane, causing it to lift and separate.
- Sagging or Depressions: These suggest structural issues or water damage that has weakened the roof’s support system.
- Water Stains on Ceilings or Walls: This is a clear sign of a leak, even if the source isn’t immediately visible on the roof itself.
- Moss or Algae Growth: While not always indicative of a leak, excessive growth can indicate poor drainage and moisture retention, increasing the risk of damage.
Weather’s Impact on Flat Roof Integrity
Extreme weather significantly impacts the lifespan and performance of flat roofs.
- Extreme Heat: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause materials to expand and become brittle, increasing the risk of cracking and failure.
- Freezing Temperatures: Water expands when it freezes, putting pressure on the roofing membrane and potentially causing cracks or damage, particularly in areas with poor drainage.
- Heavy Rainfall: Excessive rainfall can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to ponding water and increased stress on the roof membrane.
Lifespan of Various Flat Roofing Materials
Different roofing materials have varying lifespans, influenced by factors like installation quality, climate, and maintenance.
| Material | Lifespan (Years) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) | 30-50 | Durable, relatively inexpensive, easily repaired | Can be susceptible to UV degradation, less aesthetically pleasing than some other options |
| TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin) | 20-30 | Durable, reflective, resistant to UV degradation | Can be more expensive than EPDM, requires proper seaming techniques |
| Modified Bitumen | 15-25 | Cost-effective, readily available | Shorter lifespan compared to EPDM and TPO, requires more maintenance |
Flat Roof Repair Methods
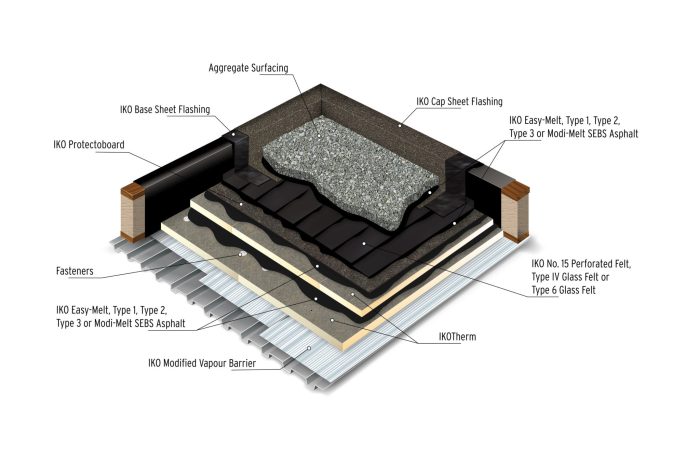
Repairing a flat roof requires different approaches depending on the type of roofing material and the extent of the damage. Understanding the specific repair method for your roof type is crucial for a long-lasting and effective fix. This section details common repair techniques for two popular flat roof materials: EPDM and modified bitumen.
EPDM Roof Puncture Repair
Repairing a small puncture in an EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber roof is a relatively straightforward process. First, thoroughly clean the area around the puncture to remove any dirt, debris, or loose roofing material. Next, carefully trim away any damaged or frayed edges of the EPDM membrane around the puncture, creating a clean, slightly larger area for the patch. Select a self-adhesive patch slightly larger than the cleaned area. Peel the backing from the patch and firmly press it onto the cleaned EPDM, ensuring complete adhesion. Finally, apply a thin bead of EPDM-compatible sealant around the edges of the patch to further enhance the seal and prevent future water penetration. This process is best performed in dry weather for optimal adhesion.
Modified Bitumen Roof Patching
Patching a larger area of damage on a modified bitumen roof is more involved. Begin by thoroughly cleaning the damaged area, removing all loose or damaged bitumen. If there is significant underlying damage to the roof deck, this needs to be addressed first, possibly requiring replacement of the damaged substrate. For the repair itself, use a modified bitumen patch, ensuring it’s compatible with your existing roofing material. Apply a layer of compatible primer to both the roof surface and the underside of the patch to improve adhesion. Heat the patch using a propane torch (carefully and following manufacturer instructions) to soften the bitumen and allow it to bond with the existing roofing. Firmly press the patch into place, ensuring complete contact. Use a roller to further smooth out the patch and ensure a solid seal. Finally, apply a layer of additional modified bitumen sealant over the patch for added protection. This should be done on a dry, warm day for optimal results.
Comparison of Repair Techniques for Different Damage Types
The approach to repairing flat roof damage varies depending on the nature of the damage. Punctures, typically small holes, are best addressed with self-adhesive patches or small sections of replacement membrane. Cracks, often caused by expansion and contraction, may require more extensive repair, potentially involving the use of flexible sealants or patching material. Blisters, which are raised areas indicating moisture accumulation, often necessitate more involved repair, potentially requiring removal of the blister and replacement of the underlying material. Larger areas of damage may necessitate a complete section replacement rather than just a patch.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Repair Materials
Choosing the right repair material is key to a successful flat roof repair.
- Self-adhesive patches: These are easy to apply and cost-effective for small punctures. However, they are not suitable for larger areas of damage or use in extreme weather conditions.
- Liquid rubber coatings: These offer a seamless, flexible repair, ideal for cracks and minor damage. They can be more expensive than patches, and require careful application to avoid uneven coverage.
- Modified bitumen patches: These provide a durable and long-lasting repair for larger areas of damage on modified bitumen roofs. They require more skill and tools to apply correctly.
- EPDM patches: These are specifically designed for EPDM roofs and offer excellent durability and weather resistance. They’re easier to apply than modified bitumen patches, but less versatile for other roof types.
Choosing the Right Repair Material

Source: co.uk
Picking the right roofing material for your flat roof repair is crucial for longevity and cost-effectiveness. The choice depends on several factors, including the extent of the damage, your budget, and your local climate. Let’s explore some popular options and how to choose the best one for your situation.
EPDM Rubber Roofing
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber roofing is a popular choice for flat roof repairs due to its durability and affordability. It’s a single-ply membrane that’s easy to install, even for DIYers with some experience. EPDM is highly resistant to UV radiation, ozone, and punctures, making it a long-lasting solution in many climates. However, it can become brittle in extremely cold temperatures and is susceptible to damage from sharp objects. Its dark color can also contribute to heat absorption, potentially increasing energy costs in hot climates. EPDM is generally best suited for smaller repairs or homeowners on a tighter budget.
TPO Roofing Membrane
Thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) roofing is another single-ply membrane option known for its excellent reflectivity and durability. TPO membranes are white or light-colored, reflecting sunlight and reducing energy costs. They are also resistant to UV radiation, punctures, and chemicals. TPO is a good choice for areas with extreme temperature fluctuations as it remains flexible in both hot and cold weather. It’s more expensive than EPDM, but its longer lifespan and energy-saving properties often offset the higher initial cost. TPO is a suitable option for larger repairs or new installations where energy efficiency is a priority.
Modified Bitumen Roofing
Modified bitumen roofing is a multi-ply system consisting of asphalt-based sheets reinforced with fiberglass or polyester. It’s a highly durable and waterproof material, offering excellent protection against harsh weather conditions. Modified bitumen is a good option for areas with heavy rainfall or snowfall, as it provides robust protection against water penetration. It’s generally more expensive than EPDM and can be more challenging to install, often requiring professional assistance. However, its exceptional durability can justify the higher cost in the long run, especially in climates with severe weather.
Decision Tree for Choosing a Flat Roof Repair Material
The best material for your repair will depend on several factors. Consider this decision tree:
1. What is the extent of the damage?
a. Small, localized damage (e.g., minor punctures, small leaks): EPDM is a cost-effective option for DIY repair.
b. Moderate damage (e.g., multiple punctures, larger areas of damage): TPO or modified bitumen may be necessary, depending on budget and climate.
c. Extensive damage (e.g., widespread deterioration, significant structural issues): Professional assessment and likely a full roof replacement are required, with modified bitumen a potential option for a full replacement.
2. What is your budget?
a. Limited budget: EPDM is the most affordable option.
b. Moderate budget: TPO offers a balance of cost and performance.
c. Higher budget: Modified bitumen provides superior durability and longevity.
3. What is your climate?
a. Mild climate: EPDM or TPO are suitable choices.
b. Extreme temperature fluctuations: TPO is a better choice due to its flexibility.
c. Harsh weather (heavy rain, snow): Modified bitumen offers superior protection.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Flat Roof Repairs
A successful repair involved using TPO to replace a section of a flat roof damaged by hail. The homeowner chose TPO because of its high resistance to impact damage and its reflective properties, reducing energy costs. The repair lasted over 10 years without any issues.
An unsuccessful repair involved a DIY attempt to patch a leak with EPDM using adhesive that was not suitable for the substrate. The patch failed within a year, leading to further water damage.
A successful large-scale repair used modified bitumen on a building in a high-snowfall area. The robust, multi-ply system successfully withstood heavy snow loads and provided excellent waterproofing for over 15 years.
An unsuccessful repair involved using EPDM in a very hot climate. The dark color of the EPDM absorbed significant heat, leading to premature degradation and cracking of the membrane within 5 years.
Preventative Maintenance and Long-Term Care

Source: abcroofingcorp.com
A little preventative maintenance goes a long way in extending the lifespan of your flat roof and avoiding costly repairs down the line. Regular inspections, cleaning, and protection from the elements are key to keeping your roof in top condition. This section discusses a proactive approach to flat roof care.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance Schedule
A proactive approach to flat roof maintenance involves a scheduled inspection regime. This helps identify minor issues before they escalate into major, expensive problems.
Inspection Schedule and Key Areas, Residential flat roof repair
A comprehensive inspection should be conducted at least twice a year – once in spring and once in autumn. Spring checks focus on damage sustained over winter, while autumn checks prepare the roof for winter’s harsh conditions. During these inspections, pay close attention to:
- Seams and Flashing: Look for any signs of separation, cracking, or deterioration in the seams and flashing around vents, chimneys, and skylights. These are vulnerable areas prone to leaks.
- Drainage System: Check gutters, downspouts, and drains for clogs, damage, or proper functioning. Ensure water flows freely away from the roof.
- Membrane Condition: Inspect the entire roof membrane for punctures, blisters, cracks, or any signs of ponding water (water pooling on the surface). Ponding water is a significant cause of damage.
- Vegetation: Remove any weeds, moss, or other vegetation that might grow on the roof surface. These can trap moisture and damage the membrane.
- Overall Condition: Assess the general condition of the roof for any unusual wear and tear, discoloration, or damage.
Cleaning and Maintenance Methods
Regular cleaning prevents debris buildup that can trap moisture and accelerate roof degradation.
- Debris Removal: Sweep or blow away leaves, twigs, and other debris from the roof surface at least twice a year. Avoid harsh chemicals or pressure washing, as they can damage the roofing material.
- Moss and Algae Removal: For moss and algae growth, a gentle cleaning solution can be used, but always test it on a small, inconspicuous area first. A stiff brush can help remove stubborn growth. Avoid aggressive scrubbing.
- Gutter and Downspout Cleaning: Clean gutters and downspouts regularly to ensure free water flow. Clogged gutters can lead to water backup and damage.
Protection from Extreme Weather
Extreme weather conditions can severely impact a flat roof’s lifespan. Proactive measures are crucial.
Snow Removal
Heavy snowfall can cause significant damage. Remove snow using a soft broom or shovel, taking care not to puncture the roofing membrane. Avoid using sharp tools or excessive force.
Drainage System Enhancement
An efficient drainage system is essential for preventing water damage. Consider adding additional downspouts or installing a more robust drainage system if necessary, especially if your roof experiences heavy rainfall.
Visual Representation of a Properly Maintained Flat Roof
Imagine a flat roof with a clean, even surface. The membrane is smooth, free from cracks or punctures. The seams and flashing around all penetrations (chimneys, vents, skylights) are neatly sealed and show no signs of deterioration. Gutters and downspouts are clean and unobstructed, leading water efficiently away from the roof. The overall appearance is one of structural integrity and cleanliness. The roof shows no signs of ponding water and is free from any vegetation or debris. This is a picture of a well-maintained flat roof, ready to withstand the elements for years to come.
Cost Considerations for Flat Roof Repair: Residential Flat Roof Repair

Source: nrc4help.com
Repairing a flat roof can be a significant investment, and understanding the factors that influence the final cost is crucial for budgeting and planning. Several variables contribute to the overall expense, ranging from the materials used to the size of the damaged area and the complexity of the repair. Knowing what to expect can help you make informed decisions and avoid unexpected expenses.
The cost of flat roof repair is influenced by a combination of factors. These factors interact in complex ways, making it difficult to give a precise estimate without a thorough assessment of the specific situation. However, understanding these factors can help you prepare a more accurate budget.
Factors Affecting Flat Roof Repair Costs
The following table outlines the key factors influencing the cost of your flat roof repair, along with explanations and examples to illustrate their impact.
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the Repair Area | Directly Proportional | Larger repair areas require more materials and labor, leading to higher costs. | Repairing a small leak versus replacing a large section of damaged roofing. |
| Type of Roofing Material | Significant | Different roofing materials have varying costs, with some being significantly more expensive than others. | EPDM rubber membrane is generally less expensive than TPO or PVC membranes. |
| Labor Costs | Significant | Labor costs vary depending on location, the contractor’s experience, and the complexity of the repair. | Specialized repairs, such as those involving complex flashing details, will cost more in labor. |
| Accessibility | Moderate | Difficult-to-access areas may increase labor costs due to the time and effort required to reach the damaged area. | A roof requiring scaffolding or specialized equipment will cost more than a readily accessible roof. |
| Severity of Damage | Significant | Minor repairs, such as patching small leaks, will cost considerably less than extensive repairs or full replacements. | A simple leak repair compared to a full roof replacement due to extensive water damage. |
| Geographic Location | Moderate | Material and labor costs can vary significantly depending on location, influenced by factors such as local supply and demand. | Repair costs in a densely populated urban area might be higher than in a rural area due to higher labor and material costs. |
| Additional Services | Variable | Additional services, such as cleaning debris or removing and disposing of old roofing materials, will add to the overall cost. | Removal of old roofing materials and proper disposal adds to the total project cost. |
Typical Cost Ranges for Flat Roof Repairs
The actual cost of a flat roof repair varies greatly depending on the factors mentioned above. It’s important to obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors to get a clear understanding of the potential cost range in your specific geographic location.
For example, a small patch repair for a minor leak might fall within a lower cost range, while a full roof replacement encompassing a large area will significantly increase the overall cost. Similarly, repairs in metropolitan areas with higher labor costs tend to be more expensive than those in less populated regions. The type of material chosen also dramatically affects the overall price, with premium materials resulting in higher costs.
Wrap-Up
Successfully repairing your residential flat roof involves a combination of careful assessment, appropriate material selection, and diligent execution. By understanding the common problems, repair techniques, and preventative maintenance strategies as outlined in this guide, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your roof and protect your home from costly water damage. Remember, regular inspections and proactive maintenance are key to preventing major repairs down the line. So, grab your tools and let’s get started!